Are you curious to know more about cold welding machine and its applications in the industry? Here’s your chance to learn all about it!
Cold welding machines are incredibly useful in the manufacturing sector, providing unparalleled fast and efficient operations. This comprehensive guide not only explains how it works but also the various applications of cold welding machines. You won’t want to miss out on this!
Cold welding is a process of bonding two surfaces in which no heat or arc is used. It is a process solely based on pressure and force, allowing two metals to be bonded and fused together with the desired strength of the bond. This type of welding creates exact parts that are free from impurities, making it an efficient solution for many applications in industrial manufacturing processes.
This guide will give an overview of cold welding machines and the processes they use, as well as its various applications in different industries. It will cover how cold welding works, what materials it can be used on, safety protocols to follow when using such equipment, benefits and disadvantages of cold welds over other techniques, types of machines available and their features, and finally cost/maintenance considerations for using cold welds for industrial applications. The goal is to provide helpful information to those who are seeking to learn more about cold welding machines so that they can make better informed decisions when selecting a machine for their manufacturing needs.
How a Cold Welding Machine Works
Cold welding machines work by using electricity to pass an electric shock through two panels or other metal surfaces. This creates a fusion between them and joins them securely. The process does not involve traditional welding, as no heat is generated, and can be used on fragile surfaces or to repair delicate components of a product.
As the name implies, unlike regular welding techniques that use heat, cold welding does not pose a risk of damaging the base material’s properties when re-forging or assembling metals.
In this method of welding, the surfaces to be welded are first coated with an electrolyte liquid solution that assists in conducting electricity, such as an acid-based solution or a magnesium alloy liquid electrode. The current then passes between the two electrochemical bonds in the panels being connected which helps in creating an instantaneous bonding effect due to kinetic energy being released during metal contact and metal surface diffusion. This results in an incredibly strong bond that is incredibly durable and resistant to corrosion and wear and tear due to electrical movement within the metal interface layers.
Additionally, cold welding can be used effectively without creating toxic byproducts, as there is no requirement for additional fluxes mixed with chemicals during the operation.
Basic principles of cold welding
Cold welding, also known as contact welding, is a heatless process that permanently joins two metal surfaces when brought together under pressure. Although no heat is involved, the surfaces of the metal objects must be cleaned of all contaminants in order to ensure a reliable bond. Furthermore, the two metal pieces must be extremely close together so that an atomic bond can take place.
The basic principles of cold welding can be summarized as follows: when two clean and closely-positioned pieces of a similar or dissimilar metal are subjected to high pressure, their atomic surfaces combine to form an interface. This effect causes the adhesion between the two objects to become extremely strong and incompressible, as well as corrosion resistant. As such, it is one of the strongest and most reliable bonding techniques available!
Cold welding applications are vast and include joining plain or precoated sheets of steel; fastening components such as brackets and flanges; fastening tubes; wiring harnesses; automobile suspension systems such as those found in race cars; aerospace applications including aircraft engines; machinery components such as gears and hydraulics; railcars weatherproofing seals and tubing systems in power boilers. In addition to its use in industrial applications, this technology has been implemented in microelectronic devices such as sensors, circuit boards, chip carriers, etc., thanks which allows for closely connected electrical connections with extreme accuracy.
Applications of Cold Welding Machine in the Industry
The use of cold welding machines composed of advanced elements has seen a tremendous increase in the industry over the past decades. The application of cold welding technology is versatile in all types of industries for joining and forming components that are traditionally impossible to weld using traditional processes like MIG, TIG or Soldering.
Cold welding is being used by almost every industry in manufacturing, fabrication & maintenance activities from regulating processes on assembly lines to precision machining, such as automotive, aviation, automotive body & component aftermarket parts production and repair work. For these purposes, the elements required are solid state bonding machines of high energy density or ultrasonic welder machines instead of conventional welding machines.
The benefit in using cold forging machine instead of MIG or TIG welders include no distortion to the part being bonded due to its linear expansion characteristics making it extremely suitable for precision operations; no filler materials are required thereby improving productivity cost-effectively; Low amounts of heat improves consistency with minimal risk to parts nearby; No sparks hence presenting better safety for personnel operating it and lastly minimal air pollution since no fumes produced.
The applications for using this type of joining technology range from medical implant manufacturing & repairs to shoe components joinery, car door panel assembling and fuel tanks treatment works. In addition, other industries such as fishing rod production uses this method quite frequently taking advantage from its ability in imparting near zero warpage and smooth surface finish after undergoing ultrasonic welding process. As well as having an ability to produce a strong joint which could be comparable as strong as a fused joint which makes them ideal for applications used marine environment where corrosion resistance is important even though aluminum can be welded together with other type materials creating perfect joints like steel or magnesium alloys ensuring highest tensile strength possible.
Electronics industry
The electronics industry requires precision and efficiency in all stages of production, and cold welding technology is no exception. Cold welding machines provide a method for joining metal components without heat or electricity for a strong, secure connection. This process has many useful applications in the electronics industry, allowing manufacturers to weld complex shapes quickly and cost-effectively.
The cold welding process works by forming a metal oxide layer between two parts that has been machined to the correct size, shape and hardness. A molecular reaction between these metals produces a strong bond while protecting the material from oxidation or corrosion caused by changes in temperature. The cold weld is held together by molecules binding at the atomic level rather than heat or electricity – thus eliminating thermal stresses that can occur with other processes such as soldering or brazing which rely on heat.
Thanks to its superior bond strength, cold welding is suitable for use with a number of materials including aluminum alloys, brass, copper, stainless steel and titanium. It is often used in the manufacturing of electronic components such as circuit boards, connectors and batteries as well as medical instruments where accuracy is paramount. Cold welding is also highly advantageous for repairs due to its fast setup time, which allows it to be used when access to power sources may be limited or not available at all.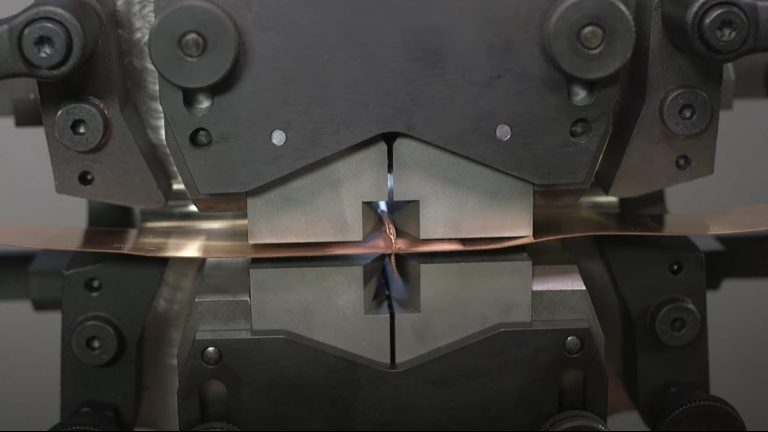
Aerospace industry
The aerospace industry utilizes cold welding machines for a variety of purposes. Cold welding technology is generally used to join dissimilar materials of varying sizes with the goal of reducing complexity and increasing production speed. Cold welding machines offer numerous advantages over traditional mechanical or adhesive processes, including superior strength and precision. This makes it an ideal choice for the demands of the aerospace industry, where complex designs and parts with high tolerance requirements are often encountered.
Cold welding in this sector has been used to join dissimilar metals such as steel, aluminum and titanium for components such as landing gear systems and airframes. The process typically produces strong, consistent bonds that meet high safety standards due to its excellent repeatability even after multiple uses. Other applications include joining high-temperature superalloys such as nickel-based & cobalt-based alloys to create turbine blades, brackets, suspender bars and other directional control components.
The aerospace industry also relies heavily on cold welding technology for microelectronics fabrication. Reduced electrical resistance at interfaces between materials is achieved—enabling miniaturization—by employing this process over alternatives such as soldering or brazing which involve a filler material that can introduce imperfections into joints or components. In addition, compared to other techniques, cold welding offers greater economy due to minimal pre-processing needed on both base materials before joining and the ability to produce parts with very tight tolerances routinely that help reduce scrap costs associated with machining operations down the line.
Automotive industry
The automotive industry is one of the biggest beneficiaries of cold welding technology. Automotive components made from cold welded metals are significantly stronger, more lightweight, and more durable than those made using traditional welding techniques. As such, they are often used in demanding applications where high performance and a long life span are critical.
One of the most common uses for a cold welding machine in the automotive industry is for creating undercut fasteners. These consist of two parts that can be pressed together in order to form an interlocking joint that is surprisingly strong. This type of joint does not require any additional components or additional processes, making it attractive for use in the manufacturing process. Furthermore, these are often used to connect aluminum panels or steel frames due to their strength and low weight characteristics.
In addition, automakers can benefit from cold welding machines through their improved strength-to-weight ratios when compared to traditional welding techniques. This can help reduce overall vehicle weight while still providing superior performance and safety characteristics – making them attractive choices for engineers looking to reduce weight while meeting critical performance requirements. Additionally, cold welded elements provide higher levels of corrosion resistance and improved fatigue life compared to traditional joining methods such as brazing or riveting. This helps reduce maintenance costs over time as well as improve overall product quality and lifespan – thus increasing customer satisfaction with their vehicles as well as enhancing total cost savings from lower fuel consumption and fewer repairs required over longer ownership periods.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cold Welding Machine
Cold welding machines offer several advantages for industrial applications. One of the biggest benefits is their ability to join metals and conductive materials without a special flux or shield gas. This eliminates some of the time and cost associated with welding processes that require fluxes and shielding gases. Additionally, cold welding offers higher joint strength because the process does not require high levels of heat, so components remain in their original state with minimal structural changes. Cold welding also creates a more localized bond with little damage to nearby components.
On the other hand, cold welding has certain limitations compared to traditional welding methods. The process typically requires components to be cleaned and highly polished while using two matching metals with very similar rates of thermal expansions and corrosion resistance, which can increase production costs. Additionally, cold welding only works on flat surfaces with low curvature, making it difficult to use for joining curved parts or components that don’t fit perfectly together. Furthermore, cold welds fail faster than regular welds due to metallurgical changes caused by the cold-welding process itself. This can potentially lead to lower-strength joints unless all process parameters are closely monitored and controlled at all times during production.
Advantages
Cold welding machines provide an efficient and effective way to weld components together without the use of heat or other external energy sources. This type of welding offers numerous advantages over traditional methods and is becoming increasingly popular in a variety of industries, from automotive engineering to aerospace technology.
The primary advantage of using a cold welding machine is the time savings it offers. Cold welding allows manufacturers to complete projects with minimal preparation time and no long cooling periods that may be necessary using traditional welding techniques. This reduces labor costs and can enable companies to meet tight deadlines or otherwise complete projects quickly and efficiently. Additionally, cold welding requires fewer skilled workers due to its simplicity, making it an economically sound investment for any business.
Another key benefit of cold welding is its accuracy level. It offers precise joining of complex components with extreme accuracy, creating surfaces that can look as if they were machined from one solid piece instead of two separate parts. This helps eliminate possible sources of failure while providing more durable parts with little room for error from the initial installation stage throughout their service life. With the ability to accurately align components, cold welding machines save manufacturers time and money in preparation before the completion of projects by ensuring minor adjustments are not required once assembly is underway.
Finally, although different applications require different materials for best results, many modern cold welding machines offer compatibility with a wide range of substrates including metals, plastics and composites; this includes difficult-to-weld materials like titanium, aluminum alloys or stainless steel. It also eliminates the need for fluxes or pre-treatment prior to joining two pieces together, eliminating additional steps needed before assembly can take place in addition to saving valuable project resources like electricity costs associated with standard processes such as arc welding or soldering engines that may be relied upon in traditional processes.
Disadvantages
Cold welding machines are powerful tools that are used to join materials including metal, plastic, glass and wood to create permanent bonds. Despite their strength and versatility, cold welding machines have some disadvantages which should be taken into consideration when deciding whether or not they are the right tool for your application.
The first potential disadvantage of cold welding machines is their cost. These tools can be expensive to purchase and may require an investment in additional components such as special fixtures and stands to optimize performance. Additionally, as these machines typically rely on electricity they may require costly ongoing maintenance or an upgrade of power cables if you are operating from a remote location.
In addition, cold welding machines require highly skilled operators that can understand how the tools work and the types of material that will work best with them. This means specialized training for those who will be using the machine and can make it difficult for those just starting out with this type of technology. Furthermore, as these machines use high force during the bonding operation there is always a risk of component damage if not used correctly. This makes it important to follow manufacturer instructions to ensure safe operations at all times.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Cold Welding Machine
When you’re in the market for a cold welding machine, it’s important to consider several factors to ensure you make the best purchase decision. Here are some of the key points to keep in mind when selecting a cold welding machine:
- Technical Parameters: Cold welding machines come with different technical parameters, including power input, rated current, and cooling system. Knowing these requirements will help you determine which model is best suited for your operations.
- Safety Features: As with any type of welding machine, safety is a critical aspect to take into account when selecting a unit. That’s why it’s important to ensure that the model you choose comes with required safety features such as over-temperature protection and overload protection circuits.
- Price & Maintenance Cost: Of course, price is always an important factor when making any purchase decision—especially when dealing with equipment as expensive as a cold welding machine. Additionally, another cost point to consider is ongoing maintenance costs associated with the unit in order to ensure optimal performance over time.
4 Portability & Dimensions: As they are usually larger than other types of welding machines, cold welders can be less portable and require more space for installation — so make sure that any room or area intended for setup meets size and access requirements before investing in any model of this particular type of equipment.
5 Quality assurance & After-Sale Services: Finally, you should consider the quality assurance offered by the manufacturer or vendor; this will demonstrate their commitment to providing reliable products and servicing them post-purchase if necessary. A reliable source of after-sale services can provide great peace-of-mind throughout your investment into using a cold welding machine in your production processes!
Material compatibility
Before you can use a cold welding machine, you need to make sure the two materials are compatible. If the materials are not compatible, then it is not possible to join them and the welding process will fail. The compatibility of welding material depends on various factors such as crystalline structure, grain size, and impact strength. Different alloys have different properties and will therefore require different approaches to ensure successful welds. Generally speaking, metals like aluminum, stainless steel and low-alloy steels are more easily welded by cold welding machines. However, higher alloy steels may require a different approach or even specialized tooling in order to achieve effective results.
In addition to metal compatibility, plastic materials like polypropylene and polyethylene may be able to be joined with a cold welder. It is important that these materials have similar chemical makeups in order for them to be successfully bonded together.
When assessing material compatibility for cold welding applications, it should also include temperature considerations as extreme temperatures often affect metallurgical properties of the material being joined together including its strength and ductility. Heat from the process can affect hardness of the weld joint so if two dissimilar metals that do not suitably join together with a standard cold welder are being used then special techniques may need to be employed such as using non-fusing methods or lower power settings on the cold welder machine itself.
Welding speed
Welding speed is an important metric when selecting the right cold welding machine. The welding speed of a cold welding machine is usually determined by the contact force and the traverse speed applied to the work-piece. The contact force determines the holding pressure for clamping of parts together. The traverse speed dictates how fast the current will flow through a joint, thus melting and forming a welded bond between materials. The higher the contact force and traverse speeds, higher welding speeds can be achieved.
Cold welding machines have different regimes to perform welds depending upon material properties and dimensions of parts being joined. Typically, there are three main cold welding regimes: localised tight spot welding, intermittent butt welding (IBW) and abutting butt-welding (ABW). Depending on why type of regime employed by cold welding machines in operation, different values of contact forces and traverse speeds can be used to produce welds with varying degrees of quality. Higher forces are employed in localised tight spot-welding while lower forces with sustained traversal motion is perfect for producing smooth surface finish in ABW applications. Thus, proper selection of right cold welding machine based upon application requirement becomes imperative when it comes to achieving desired results within stipulated time.
Conclusion
The cold welding process offers many advantages when compared to conventional welding processes. This technology is an eco-friendly, safe and efficient way to weld an array of metal and plastic components together. It’s a fast process and very cost effective, as it eliminates the need for costly tempers, fluxes, and soldering alloys.
Cold welding machines can be used in various industrial and commercial applications, including automotive assembly lines, aviation manufacturing, computer parts fabrication and nuclear power plants. With the development of new machines and tools to help streamline the process even further, this technology is sure to have a rapid growth over time.
FAQ’S
How does cold welding machine work?
A cold welding machine works by using high pressure to join two pieces of metal together without the use of heat or filler material.
What are the application of welding in industries?
Welding is used in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and shipbuilding, among others.
What machine is used for cold welding?
A cold welding machine, also known as a pressure welder or a friction welder, is used for cold welding.
What is application of welding machine?
Welding machines are used for joining two or more pieces of metal together in a variety of applications, such as construction, manufacturing, and repair work.
What are the advantages of cold metal transfer welding?
The advantages of cold metal transfer welding include reduced heat input, less distortion, reduced spatter, and improved control over the welding process.
What causes cold welding?
Cold welding is caused by the bonding of two clean, flat metal surfaces under high pressure, resulting in atomic diffusion between the two surfaces.
What is the physics of cold welding?
The physics of cold welding involves the process of atomic diffusion, which occurs when two clean metal surfaces are brought into contact under high pressure.
How does cold metal transfer welding work?
Cold metal transfer welding works by using a pulsed current to transfer small droplets of metal from the electrode to the workpiece, resulting in a low-heat, low-spatter welding process.
What is the difference between cold and hot welding?
Cold welding occurs at room temperature without the use of heat, while hot welding involves the use of high temperatures to join two pieces of metal together.
What are the four applications of welding process?
The four applications of welding process include fusion welding, solid state welding, brazing, and soldering, each with its own unique set of advantages and limitations.
See more-
- Best cold welding machine 2023
- Best auto darkening welding lens 2023
- Best pants for welding 2023
- Best tig welding gloves 2023
- Best welding boots 2023


